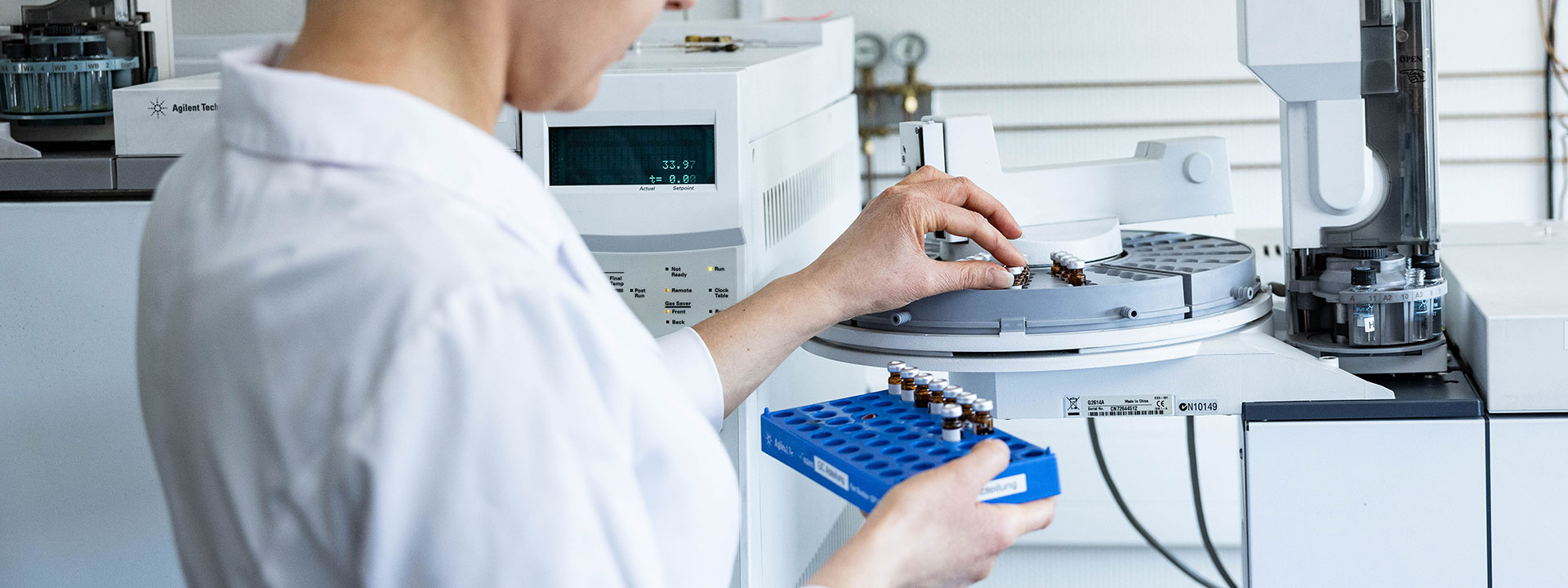
GC-VUV
Analysis of Mono- and Di-aromatics in Jet Fuel (GC-VUV)
- Quantification of Aromatic Compounds in Jet Fuel and SAF according to ASTM D8267
- PIONA and Oxygenate Analysis of gasoline according to DIN EN 18015 or ASTM D8071
- Verified Hydrocarbon Analysis (VHA) of gasoline and naphtha according to ASTM D8369 (cf. DHA according to ASTM D6730)
- Analysis of Waste Plastic Process Oil (WPPO) according to ASTM D8519 (expected from Spring 2025)
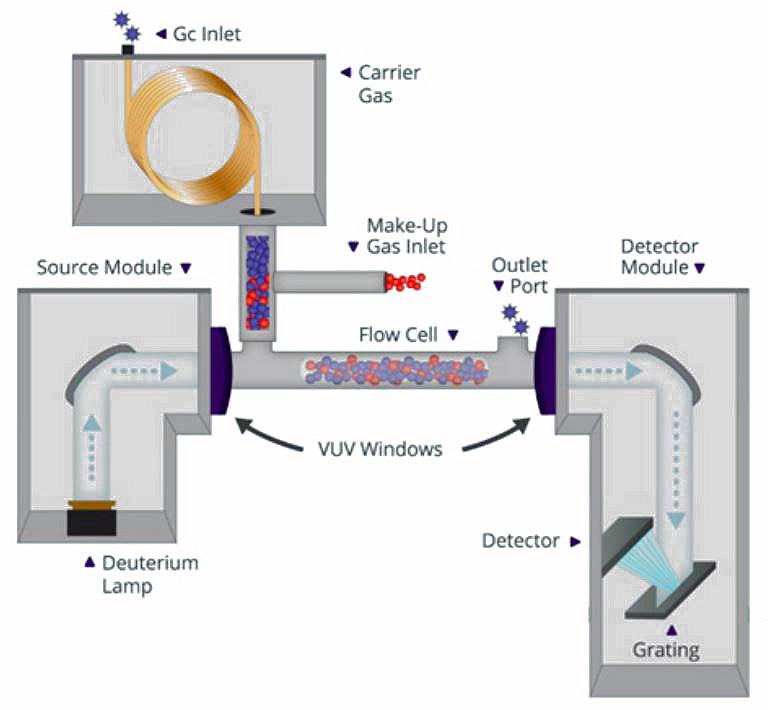
Schematic Layout of the VUV Detector
Chromatogram of a Conventional Jet Fuel
The absorption of saturated compounds from 125 – 160 nm is marked in red, while the absorption of aromatic compounds from 170 – 200 nm is marked in green. Based on the characteristic absorption ranges, mono- and di-aromatic compounds are identified.
Using specific response factors, the detected absorptions can be directly converted into mass or volume percentages.
Need help selecting the right GC method?
Carbon number: C5 - C12
Boiling range 35°C - 210°C
PIONA and
relevant Oxygenates
ASTM D8071
GC-VUV
prEN 18015
GC-VUV, Alternative for EN 22854 (Reformulyzer)
ASTM D8369
GC-VUV (VHA)
Carbon number: C10 - C22
Boiling range 170°C - 370°C
Heating Oil, Diesel, Jet A1, SAF
ASG 2502
GC×GC-FID
ASG 2253
GC×GC-MS
ASTM D8267
GC-VUV
Mono- and di-aromatics as sum parameters, Alternative to ASTM D6379
Carbon number: C17 - C55
Boiling range 300°C - 600°C
ASG 2501
HT-GC×GC-FID
ASG 2221
HT-GC×GC-MS Screening
Carbon number: C5 - C64
Boiling range 35°C - 630°C
ASTM D8519
GC-VUV
Need additional analyses?
Our laboratory has been accredited since 1998 for the analysis of numerous fossil and biogenic fuels.